Vendor Impersonated in Invoice Fraud Attack
Vendor email compromise, in which a compromised vendor sends invoice or payment attacks to their customers, is growing in popularity. An easier to detect method of this attack happens when a vendor is impersonated, rather than compromised. In this attack, the threat actor is impersonating a known vendor in order to receive payment for a fraudulent invoice.
Summary of Attack Target
- Platform: Office 365
- Email Security Bypassed: Proofpoint
- Victims: Employees
- Payload: Malicious Link
- Technique: Impersonation
Overview of the Vendor Impersonation Attack
This organization communicates often with a known vendor. Recently, an employee from the accounting department received a message from what appeared to be the Assistant Controller / HR Administrator for this vendor. In the message, they were notified of an overdue invoice. In actuality, however, the attacker had registered a domain similar to that of the real vendor but changed the name slightly—for example, the real vendor might have been at acmehomes.com, but the attacker registered acmehome.com, omitting the s in the domain.
The email states that there is an unpaid invoice, which must be paid to an updated bank account. The attacker alleges that their financial institution has changed as a result of the current pandemic and the suspicious sender then states they will send over the updated bank information once the recipient replies.
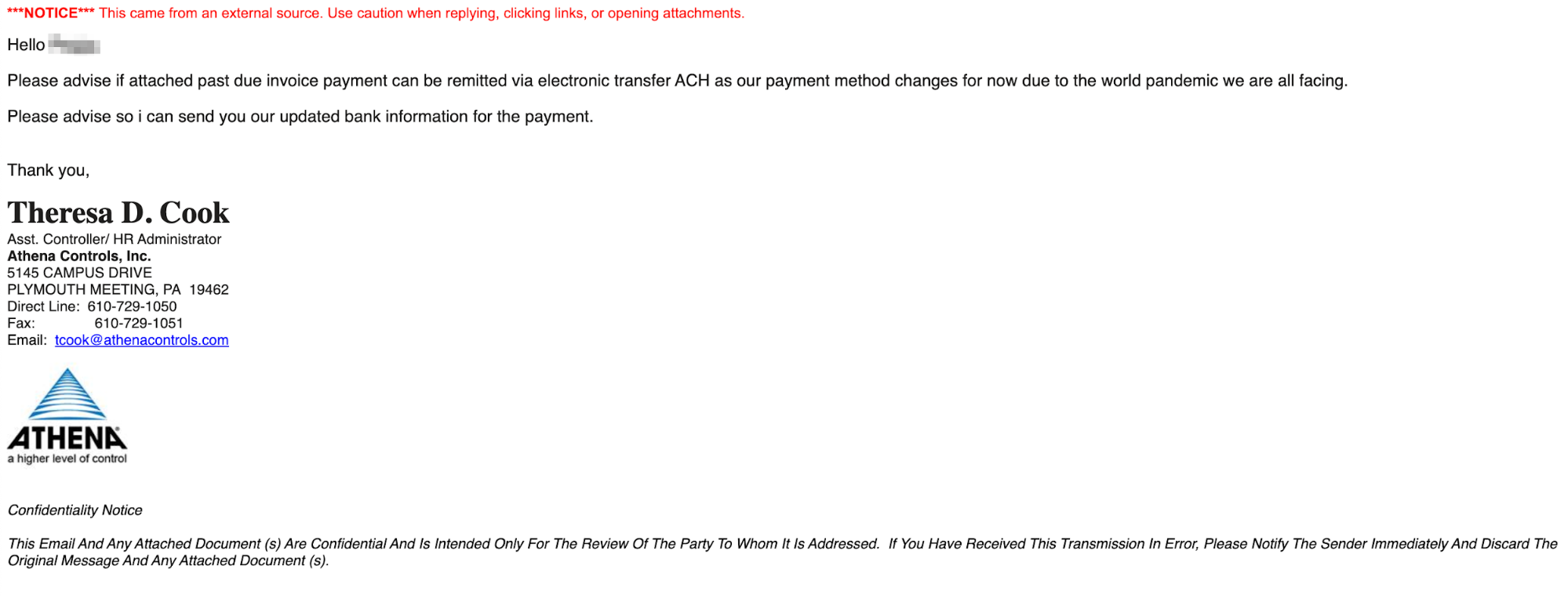
Should the recipient have fallen victim to this attack and made the payment, the organization would have had a significant financial loss and potentially opened itself up to more fraudulent exchanges in the future from the same attacker.
Why the Vendor Impersonation Attack is Effective
This attack leverages the COVID-19 pandemic as an excuse for the fraudulent payment update. The attacker injects urgency into the message by claiming there is an issue of a late unpaid invoice. The attack also impersonates a high-level employee and targets payroll and accounting employees who, because they expect legitimate invoices, may be less likely to scrutinize the sender information and attached invoices.
In addition, the attacker's email came from a domain that looked like the domain of the real company. The email domain the message was sent from was recently registered by the attackers with a slight difference. Further, the registrant information was not consistent with the real vendor, though anyone receiving the email would have had to spend a good deal of time digging into this information to discover it.
As an added element, the invoice attached to the email looked like a real invoice from the legitimate vendor, including their logo, their real address, and other real information.
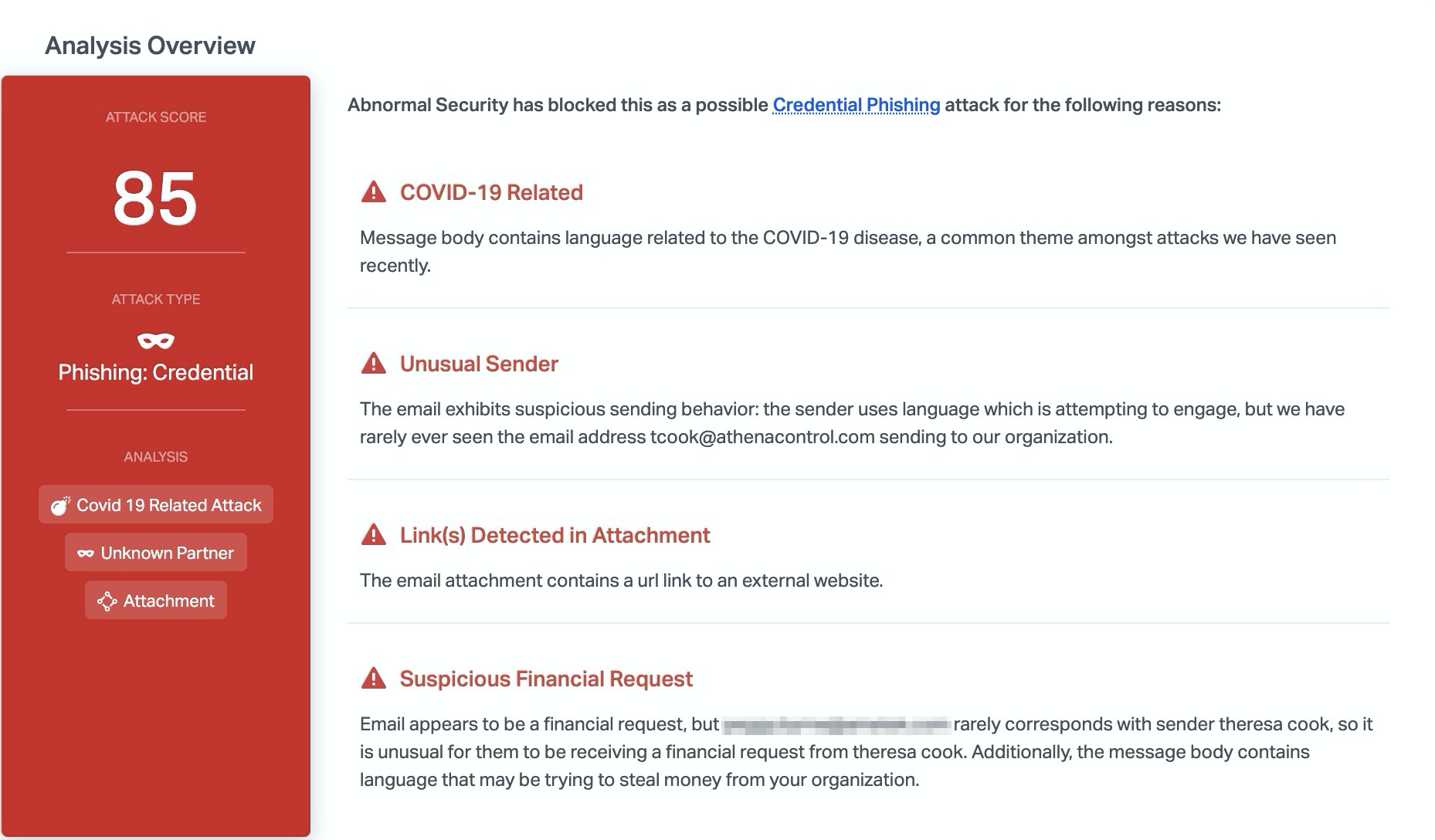
Abnormal detected this fraudulent email due to to the unusual sender address and the suspicious financial request. Because the recipient had never interacted with this person, it was unusual for them to receive a financial request. Combined with the urgency of the email and the mention of the pandemic, it is clear that this email is malicious and Abnormal blocks it before it reaches inboxes.
To see how Abnormal can protect you from fraud in your supply chain, see a platform demo today.






