Fake RFQ Used in Malware Attack
A request for quote (RFQ) continues to increase in popularity as an attack type, as vendors are likely to open the attachments or click the links associated with these types of email. In this attack, attackers disguise harmful malware as a RFQ to encourage recipients to download the dangerous files.
Summary of Attack Target
- Platform: G Suite
- Victims: Employees
- Payload: Malicious Link
- Technique: Impersonation
Overview of the RFQ Malware Attack
This attack is an impersonation of a “request for quote” (RFQ) from a legitimate, outside organization. The attack originates from the throwaway address “info@req-allparts.com”, with the reply-to address “glennmauldin@zidnei.com”.
By using urgent language, the attacker attempts to coax the recipient to click on the link “Rfq 507890.pdf” without examining it for malicious content. Clicking on the link does not download a PDF or bring the recipient to an external website, but rather forces a malware download.
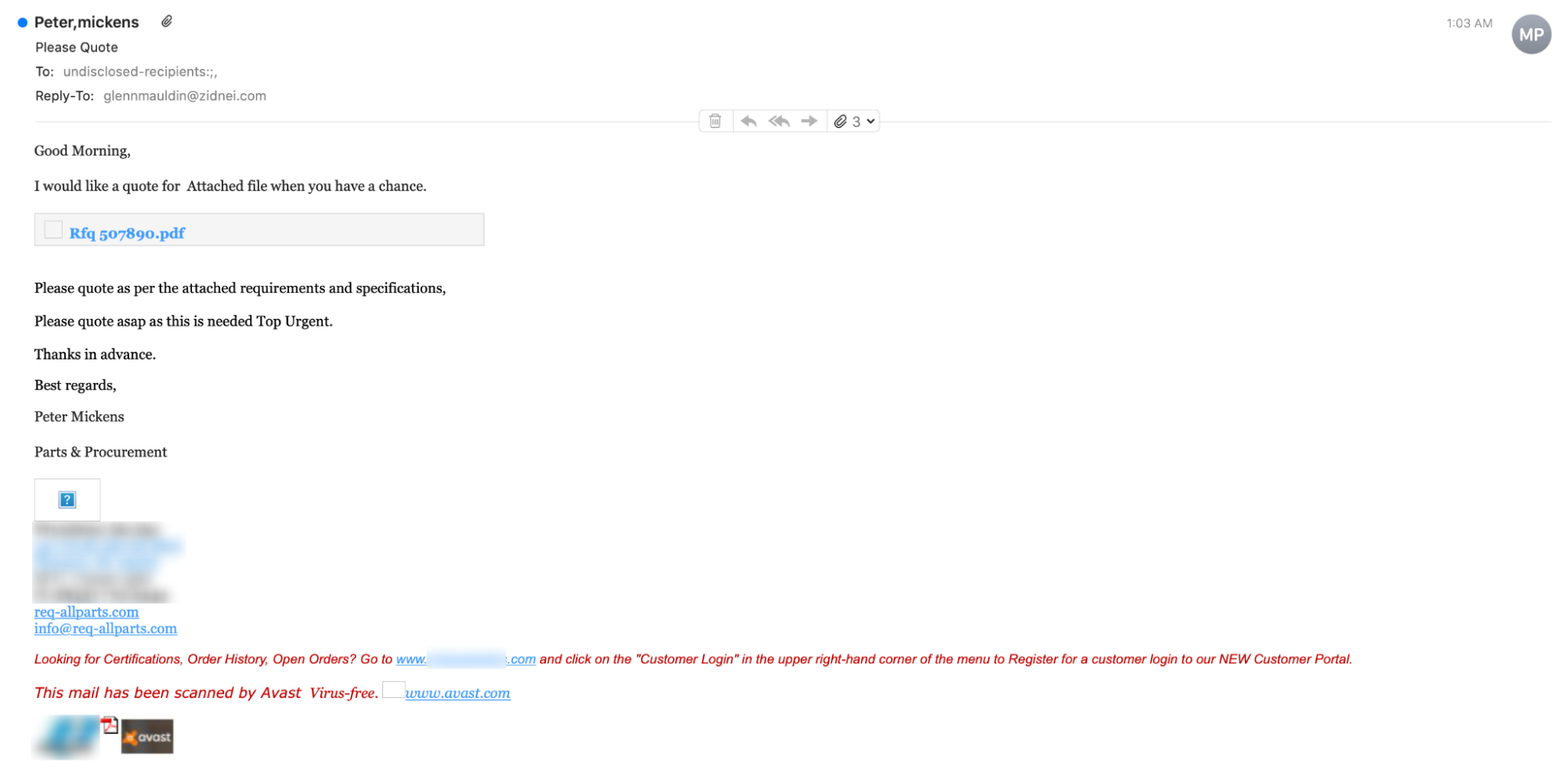
The downloaded file from the malicious link is a compressed .GZ file, which enables it to circumvent certain malware detectors. Within the compressed file is a text file full of malicious code, including spyware such as a keylogger. If the recipient allows this code to run, the attacker could record everything that the recipient enters into his or her computer or possibly even take complete control of the recipient’s device.
Why the RFQ Malware Attack is Effective
The recipient of this email is likely to open this attachment, given that they believe it to contain information about a RFQ. In addition, many security systems can only detect malware if it is attached to an email in an uncompressed form. Putting malware into a .ZIP folder or a .GZ archive can easily circumvent these security measures.
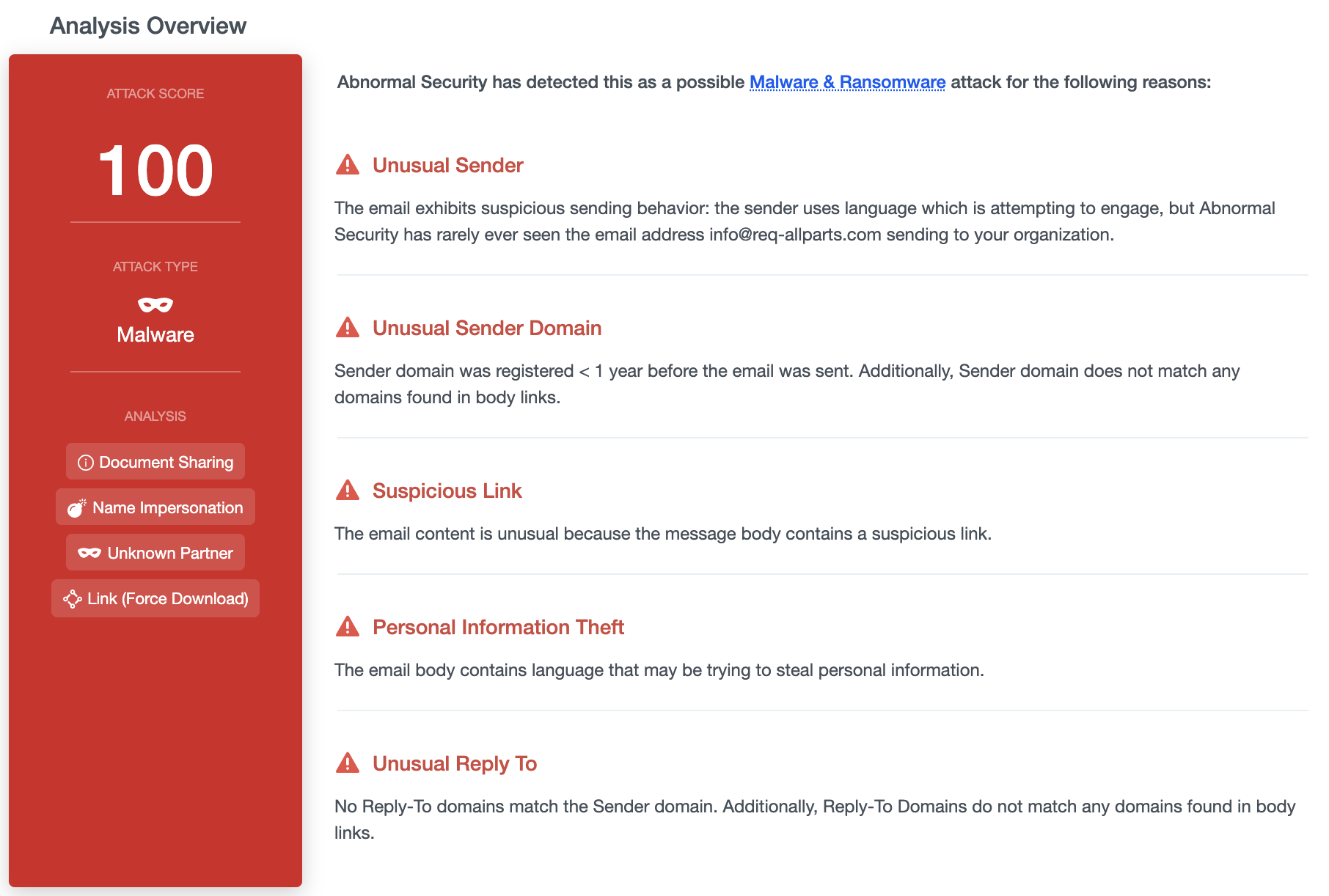
Abnormal Security prevented this attack by recognizing a number of signals that, when combined, flagged the email as malicious. Some of these signals are contained in the message body, such as the presence of suspicious wording. Others are contained in the message headers, such as the fact that the reply-to address for this email did not match the sender address or any of the links in the email. It is much more difficult for an attacker to hide these kinds of signals than it is to hide the malware.
To learn how Abnormal Security can protect you from malware attacks that others miss, request a demo today.






