AT&T Impersonated in Malware Download Attack
It’s common practice for companies to send notification emails with purchase receipts and tracking information, especially for purchases that are on the expensive side. However, for individuals who have not made recent purchases, this can be alarming, as these emails could signal fraudulent charges to the user’s credit card.
In this case, an attacker spoofed a notification email from AT&T. The goals was to encourage the target to investigate these charges, and by doing so, to inadvertently download malware.
Summary of Attack Target
- Platform: Microsoft Office 365
- Email Security Bypassed: FireEye
- Victims: Employees
- Payload: Malware
- Technique: Spoofed Email + Impersonation
Overview of AT&T Impersonation Malware Attack
The email appears to be an automated notification regarding the order status of a recent purchase. The sender email looks like it comes from an authentic AT&T email address, and the images embedded in the body are the same as those used by the brand. However, checking the header IPs of the email, we are able to verify that the sender information is spoofed. We would expect the IP of an authentic email from AT&T to come from AT&T. This email, however, originated from an IP address in Ghana.
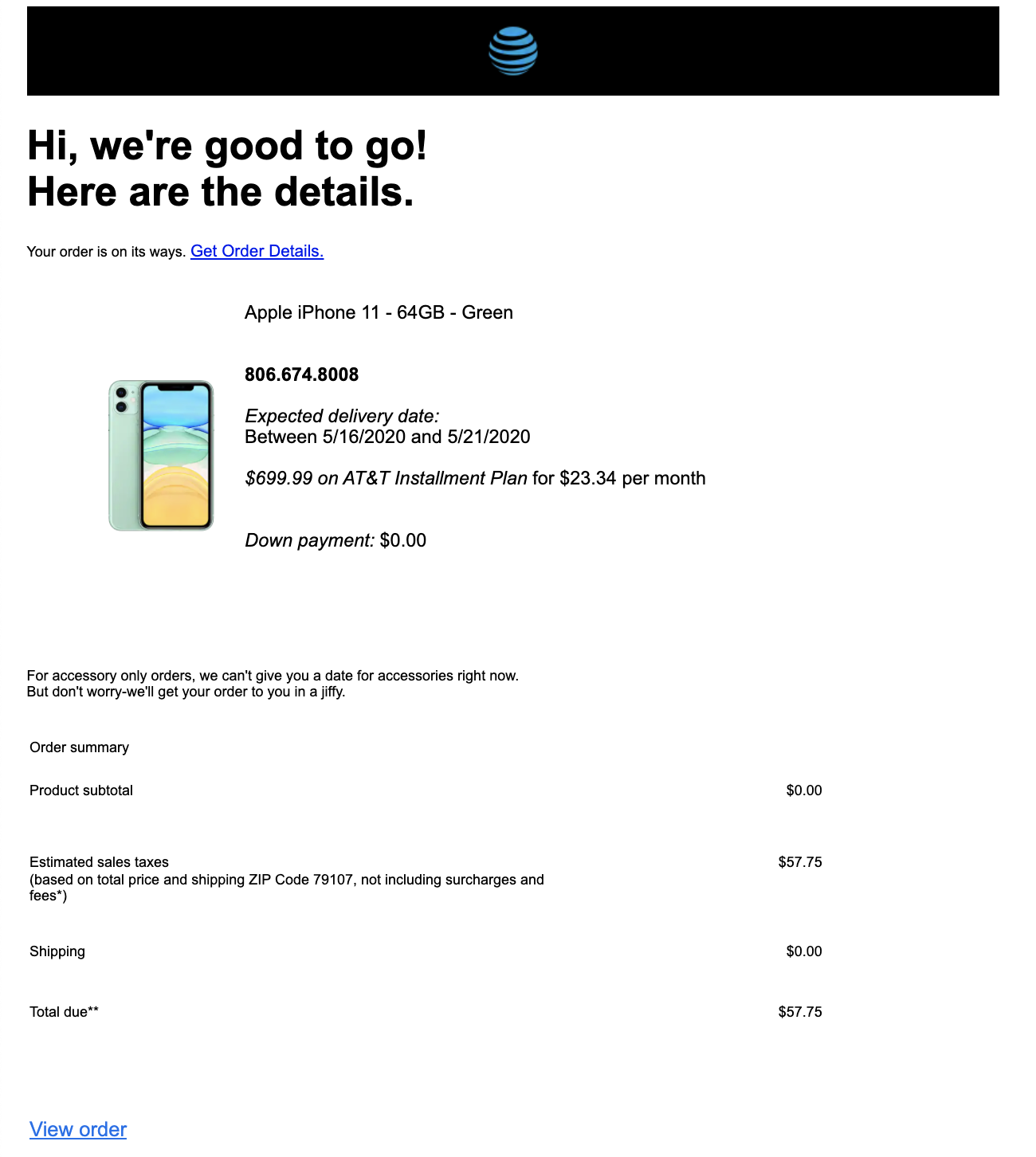
The email contains a link claiming to be the order details of the transaction. However, clicking on the link automatically downloads a .jar file that contains malware. The download is hosted at a site that is commonly used to store various malware downloads.
Should recipients fall victim to this attack, their device would be infected with malware. This would allow the attacker to steal sensitive personal information and potentially hijack the user’s device.
Why the AT&T Impersonation Malware Attack is Effective
The sender email was spoofed to impersonate a legitimate email address used by AT&T Wireless to send tracking notifications to customers. The email body itself perfectly matched legitimate emails sent by this AT&T email address—the formatting, the embedded images, and the content were identical. The only differences were the links attached to the email. The attacker anticipates that since the sender and the email appear authentic, recipients would be less suspicious of the downloaded malware file.
In addition, the malware URL is wrapped with text in the email body in order to conceal the link used by the attacker. The link directs to a download hosted at a page the attacker likely controls which is not affiliated with AT&T.
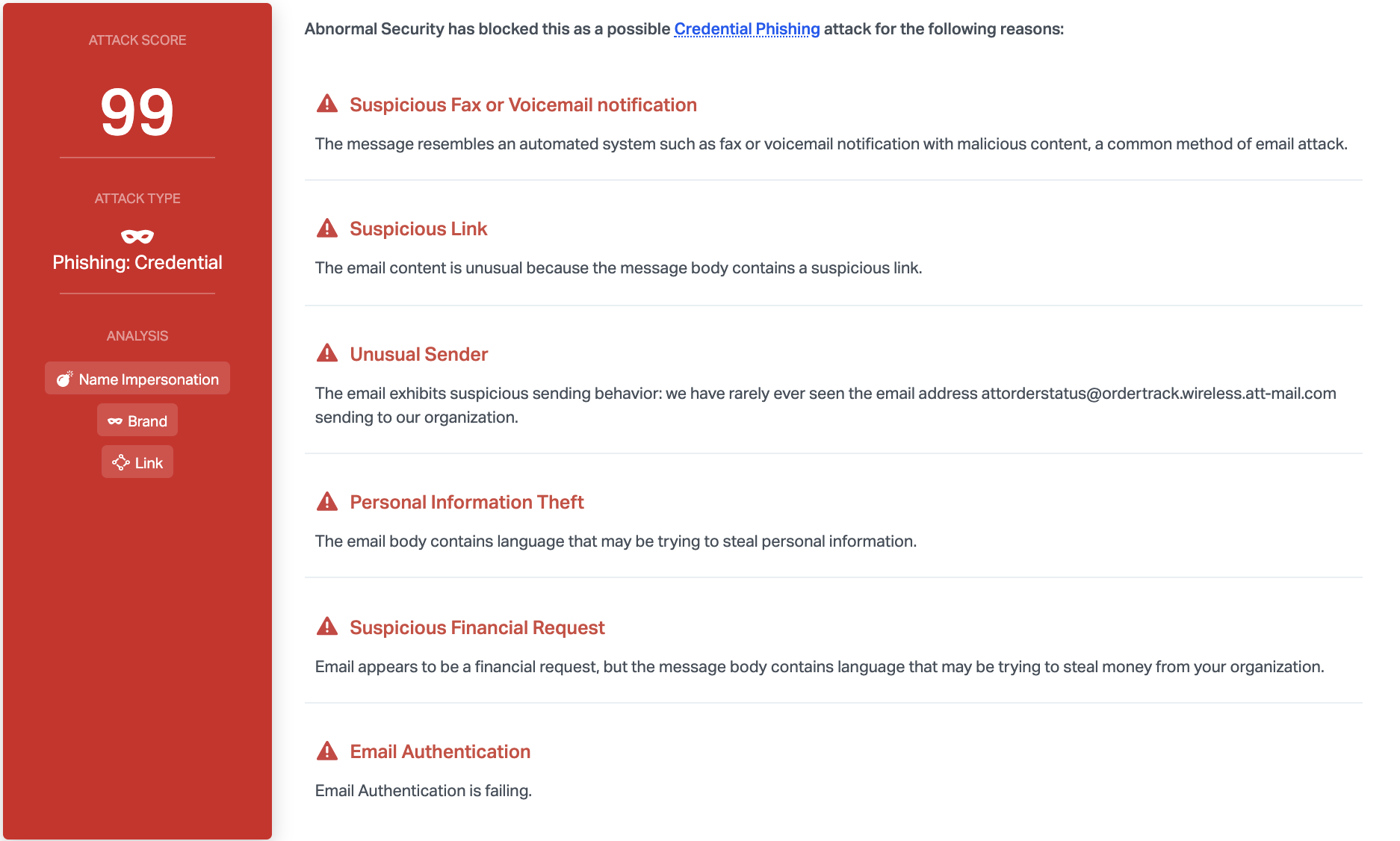
Abnormal can detect this attack as a result of a variety of factors. Most notably, DMARC email authentication fails for the sending address, and the sender has never before sent to anyone within the organization. Furthermore, content analysis shows that there is a suspicious link and that the message appears to come from an automated system, which is common method of email attack.
To discover more about how Abnormal can protect your organization from malware and other advanced attacks, see a demo today.
Get AI Protection for Your Human Interactions







